Abstrict
Pakistan is a polio endemic country as stated by Global Polio Eradication Initiative. Number of polio cases increased in last few years especially in KPK and tribal areas. Present study was focused to collect opinion regarding information, perception and practices about polio among residents of village Sohan. A sample of 100 was interviewed. Data was entered and analyzed in SPSS. A dominant majority consider polio is treatable. Vaccination helps to get healthy and, risk increased by lack of immunization. Practices represent that 94% vaccinated their children, 89% cooperated with polio teams at the time of survey, and 35 parents reported that they refused polio teams at least once in their life. Study concludes that awareness, perception and practices regarding sensitivity of the topic are very much clear to respondents, and majority fulfilling their responsibilities being a parent and also being a citizen of Pakistan.
Keywords
Polio, Polio Eradication, Polio Vaccination, Poliomyelitis, Polio and Pakistan
Introduction
The outbreak of poliomyelitis in 20th century was outrageous because of its effects, that it left thousands of children with paralysis every year. The vaccine was developed by mid of 20th century but still its adoption, globally, was not the same. The developed region considered it a public health issue and took intensive measures to get rid of poliomyelitis. A contradicting environment was found in developing region. The reason appeared to be following: They were deprived of basic necessities, like: Food, shelter, clothing etc. Health was considered a luxury and developing stereotypes about polio vaccine might be the obstructions and lead to increased number of cases. Because of above few described reasons from many, despite with investments by National immunization programme, developing region is still in struggle to eradicate polio, including Pakistan, Nigeria and Afghanistan (Polio Eradication Initiative 2017).
Poliomyelitis is caused by polio-virus which has proved to be outrageous for developing countries. The only strategy to get rid of poliomyelitis is to have strong immunization against it through “vaccination”. Several organizations (international, national, governmental) are making efforts in collaboration at different levels to get rid of such infectious disease. Because it disrupts whole environment and increases dependency ratio in society. The increase in cases of polio is because of attitude of recipients against vaccination. It also reflects that we have miles to travel to bring a sea change into the attitudes of people. It is found an obstruction Particularly in rural areas. Unawareness, developing stereotypes about vaccination, influence of social and cultural factors are all leading to an increased number of polio cases (Khan et al., 2015).
Historical Background
The infectious disease was found an endemic for the United States. As, it was first found in 1952 in the US with 58,000 cases, out of which 3,000 people died and others who recovered from it were found with disability. After 3 years of its outbreak, Dr. Jonas Salk developed a vaccine against it. After several experiments, it was given to infected people and it was found worthy. The ratio of polio cases dropped and 910 people were found infected in 1962. Thus, vaccine was found effective and cases reduced to 99%, since 1988 (Polio Eradication, 2017).
Polio and Pakistan
Polio Eradication Programme is working effectively in Pakistan since 1994 to eliminate poliomyelitis. This Programme is obsessed with the largest network. It constitutes of health experts, 260,000 workers and several laboratories. This network of people is working effectively from maintaining data and its analysis to providing vaccines as well (End Polio, 2019).
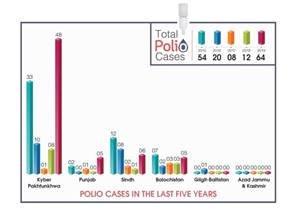
Table1. WPV Polio Cases across Pakistan’s Provinces
|
Province |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
|
Punjab |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
12 |
2 |
|
Sindh |
12 |
8 |
2 |
1 |
30 |
17 |
|
Khyber
Pakhtunkhwa |
33 |
10 |
1 |
8 |
92 |
20 |
|
Balochistan |
7 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
12 |
11 |
|
Gilgit-Baltistan |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Azad
Jammu & Kashmir |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
ICT |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Total
Polio Cases |
54 |
20 |
8 |
12 |
146 |
50 |
Source: https://www.endpolio.com.pk/polioin-pakistan/polio-cases-in-provinces, access
date 13-06-2020
COVID-19, Polio Vaccination and Pakistan
Polio is still prevailing in Pakistan although it was closer to having a polio free environment. It was because of abolition of nationwide campaigns due to which around 40 million children missed their vaccine. Halt in campaigns was because of outbreak of corona and other infectious diseases, so that its resources could be used to combat those. Ultimately, the cases in 2018, that were 12 increased to 147 last year. At the same time, another virus was found rising although the perception about that P2 strain was that it was elimination in 2014 (Baloch, 2020).
Janjua (2020) cited that halt in this service have put several lives at risk. Vaccination for diseases like polio and measles was stopped to use those resources to combat outbreak of COVID. He elucidated that several health experts have warned about another wave of infectious diseases (including polio) along with corona. As number of polio cases is also increasing which is clear from the statistical figure that 12 cases in 2018 increased to about 147 registered cases last year. Janjua (2020) further stated that halt in this service have put several lives at risk. Statistics show that number of cases is increasing constantly in Pakistan and about 47 cases were reported to date. Furthermore, cancellation of providing vaccine service is threatening for children accompanied by halt in service of other vaccines. He elucidated that several health experts have warned about another wave of infectious diseases (including polio) along with it.
Another study by the researchers of Johns Hopkins University, stated that around 42,000-192,000 children could die monthly because of unavailability of proper food and health services during pandemic of corona virus. This number is just because of impact of corona, excluding number of the expected death rate due to unavailability of other vaccines. This study further projects that Pakistan might encounter the 3rd largest number of extra child losses of 118 nations measured, behind India and Nigeria (Roberton et al., 2020).

Since outbreak of COVID-19 in Pakistan, the figure of children who’d missed their vaccine is not known. But EPI programme have now offered vaccines against 10 diseases where they’ve targeted around 7.9 million children and pregnant women. These diseases along with polio include pneumonia, tetanus, hepatitis-B, diarrhea, diphtheria, measles, tuberculosis, whooping cough and meningitis (Mukhtar, 2020). After the emergence of COVID-19, panic and condition of stress persuaded everywhere, a coerce against polio arose. Several important figures including Rana Muhammad Safdar who was coordination in campaign for Polio Eradication, elucidated that as a reaction to that drive, around 40 million children did not get their vaccination (Basharat, 2020).
Several research studies were conducted before to examine the influence of socio-cultural factors on recipients in Pakistan but most of them are from tribal areas, KPK, southern Punjab, agencies and also from Karachi. In addition, this study was planned to cover the opinion regarding knowledge, perception and practices of residents of village Sohan living near to Capital of Pakistan and try to conclude in relation to previous studies.
Materials and Methods
Methodology
Descriptive research wishes to correctly and scientifically describe a populace, condition or occurrence. It tries to answer “what”, “when”, “where”, “when” and “how” questions but not “why” questions (McCombes, 2019). For the sake of present study, descriptive research methodology technique was implemented for information collection.
Locale
Present study was conducted in village Sohan of Islamabad, situated near Faizabad. Most of the population of village Sohan were settlers while a big number of residents are of Pathan, Afghan, Potohari, and Punjabi ethnicity. Availability of health services, provision of basic necessities of life followed by quick transportation for main urban hubs of Islamabad is easily available from here. Literacy rate is quite appreciative. Small business community is also main feature of this community.
Research Tool
To conduct this study, open ended interview guide was developed. To collect the opinion of general public about the efficiency and effectiveness of Polio eradication campaign along with perception constructed by the society about Polio vaccine. Along with this field notes were taken where needed.
Study Sample
A sample of 100 was purposively interviewed from village Sohan. Inclusion criterion was, mother or father having at least one child less than five years of age at the time of study and experience at least one polio vaccination campaign.
Study Duration
From the mid of March-2020 to 30-May-2020 was the schedule duration of study. Initially a pilot activity was done to get some basic information about community and a community profile was developed with the help of local political figures. At second stage a list of families having at least one child under five was made and at third phase data collection was started.
Data Management
Data was collected in form of observation, arguments, and case studies to describe the point of study. Quantitative data was edited, coded and then entered into SPSS for further analysis and tabulation. Observation, arguments and descriptions are analyzed by using narrative analysis techniques. Efforts were also made to describe the relationship between qualitative and quantitative data of present study in the light of existing literature.
Ethical Consideration
Ethical challenges of the study include informed consent of the participant, confidentiality and anonymity, impartiality and potential impact of researcher and participant on each other (Sanjari et al., 2014). Each and every respondent of the study along with village political and religious figures were informed about the objectives of study. After that before data collection verbal consent was ensured.
Unit of Analysis
Unit of analysis for present study was the individuals of community and persons from health care department. A person from a family having at least one child less than 5 years; either he is willingly for vaccine to his/her child or by force were selected as unit of study.
Results and Discussion
Table 1. Demographics
|
Question |
Categories |
n |
% |
|
Age |
18-20 |
35 |
35 |
|
21-25 |
22 |
22 |
|
|
26-30 |
20 |
20 |
|
|
31-35 |
14 |
14 |
|
|
35-45 |
9 |
9 |
|
|
Qualification |
Illiterate |
15 |
15 |
|
Primary |
18 |
18 |
|
|
Secondary |
32 |
32 |
|
|
Higher
Secondary |
14 |
14 |
|
|
Intermediate
and above |
21 |
21 |
Table 1 presents the age and qualification of the study respondents. Age categories explain that 35percent of the sample was between age 18-20 years, 22percents belongs to 21-25 years of age, 20percent from age group 26-30 years and, rest from 31 years and above. Education section unveils that 15percent of our sample have no formal education while 18percent reported primary education. Secondary is come up with highest percentage and that is 32percent.
Table 2.
Knowledge about Polio
|
Question |
Category |
n |
% |
|
Did you know what Polio is? |
Yes |
92 |
92 |
|
No |
1 |
1 |
|
|
Don’t
Know |
7 |
7 |
|
|
Source of knowledge about Polio |
TV |
55 |
55 |
|
Doctor |
26 |
26 |
|
|
Imam
Masjid |
4 |
4 |
|
|
LHW |
13 |
13 |
|
|
Other |
2 |
2 |
|
|
Polio is a Health Issue |
Yes |
81 |
81 |
|
No |
4 |
4 |
|
|
May
Be |
3 |
3 |
|
|
Don’t
Know |
12 |
11 |
|
|
How Polio affects your children |
Permanent
physical disability |
93 |
93 |
|
Temporary
physical disability |
5 |
4 |
|
|
Don’t
Know |
2 |
2 |
|
|
How Polio Spread |
By
drinking water |
51 |
50 |
|
By
food |
31 |
31 |
|
|
Contaminated
food or water |
8 |
8 |
|
|
By
Air |
7 |
7 |
|
|
Don’t
Know |
3 |
3 |
|
|
Polio is treatable |
Yes |
91 |
91 |
|
No |
2 |
2 |
|
|
May
be |
7 |
7 |
Table 2
Table 2 is used to describe the awareness or prevalence of knowledge among respondents of present study about the polio. Study explains that 92 percent of respondents reported that “yes” they know what polio is while on the other hand 7 percent state that they do not know what is polio? The table further describes that 55 percent of the sample states that their major source of information about polio is TV. In 26 percent cases it was noted that they heard about polio from doctors or health care providers. However, 4 percent responded that source of information was Imam Masjid and, in 13 percent cases they heard about Polio from LHW. Majority of responses reported that “yes” polio is a health issue [81 percent]. Moreover 4 percent shared that they do not think that polio is health issue while 3 percent were of the view that maybe polio is a health issue but they never know exactly. In 11percent cases, respondents said that do not know that polio is a health issue. 93 percent of the study respondents responded that polio may lead to permanent physical disability while 4 percent said that polio cause temporary physical disability in children. In case of how Polio spread; 50 percent respondents referred that by drinking water polio is spread among people while 31 percent respondents shared that they think polio spread by taking food. However, 8 percent of respondents argued that polio is spread by taking contaminated food or water while 7 percent argued that polio is spread through contaminated air. Polio is treatable or not? 91% of the respondents argue that polio is treatable while 2% do not know that polio is treatable and 7% of respondents said that maybe polio is treatable. This shows that majority of the respondents know that Polio is treatable.
Table 3.
Perception of Respondents
|
Question |
Category |
n |
% |
|
Perception about Vaccination |
Good
for our child |
89 |
89 |
|
It
will effect fertility issues |
3 |
3 |
|
|
May
be Harmful for children |
3 |
3 |
|
|
No
response |
5 |
5 |
|
|
Lack of immunization increased risk factor |
Yes |
77 |
77 |
|
No |
33 |
13 |
|
|
May
be |
10 |
10 |
|
|
Contact with affected person will increase
risk |
Yes |
48 |
48 |
|
No |
32 |
32 |
|
|
May
be |
20 |
20 |
This table is used to explain about the perceptions of people about the vaccination of polio. 89 percent respondents said that polio vaccination is good for our children’s health while on the other hand, 3percent said that it effects fertility issues. In addition respondents were asked about the association between lack of immunization and increased risk of polio and the responses are; 77 percent were in favor of the question while 13 percent said “no” it never increased the risk of polio. Is it spread by contacting other affected persons, “yes” was recorded in 48 cases followed by 32 respondents who said it never transmit from one person to other.
Table 4.
Practices
|
Question |
Category |
n |
% |
|
Vaccination of your child |
Yes |
94 |
94 |
|
No |
2 |
2 |
|
|
Don’t
Know |
4 |
4 |
|
|
Cooperate with Polio team |
Always |
89 |
89 |
|
Some
time |
8 |
8 |
|
|
No
response |
3 |
3 |
|
|
Refused Polio team at least one time |
Yes |
35 |
35 |
|
No |
61 |
61 |
|
|
Don’t
Remember |
4 |
4 |
|
|
Last vaccination |
Before
COVID-19 |
85 |
85 |
|
Don’t
Remember |
12 |
12 |
|
|
I
was not here |
3 |
3 |
|
|
Decision maker for Vaccination |
My
self/mother |
51 |
51 |
|
Husband/father |
30 |
30 |
|
|
Father-in-law |
12 |
12 |
|
|
Mother-in-law |
7 |
7 |
Data of the above table shows that 94 percent of respondents vaccinated their children against polio spread while 4 percent said that they do not know about vaccination being out of home. In 89 percent cases respondents reported that they always try to cooperate with the polio team and that is a more than satisfactory attitude of general public while 8 percent said that sometimes they cooperate with the polio team. Table further represents that 35 percent of the respondents said that ‘yes’ they refused polio team one time in their lives, while on the other hand majority of the respondents [61%] do not refuse polio team at least one time in the vaccination history of their children. Interestingly when they were asked about the last vaccination, 85 percent responded that last vaccination of polio is used before COVID-19. In 12 percent cases they do not remember the last vaccination. Although 3% of respondents said that I was not there for last vaccination. Very important social aspect of our society is, who is the decision maker in your family? Sohan is a rural area but has the basic facilities of life with better literacy rate. Data shows that females/mother of the kid was main decision maker in case of polio vaccination [51%], and father is the second with percentile 30. Participation also reported from both in-laws with different percentages.
Previous studies show that any society is specified due to its culture, which makes it distinct from other societies. Culture reflects beliefs of people who belong to it. Culture of rural areas differs from that of urban. As people from rural areas possess specified believes that are difficult to alter. People from countryside are generally orthodox because they resist changes in their culture (Ali et al., 2018). Similarly, the perceptions of people in rural areas differ from that of people in urban areas. When research was conducted, several myths were found among people regarding use of vaccine among people. Their belief about vaccine was that, it could bring harmful effects to their children’s health instead of providing immunity against diseases. They believed that it could bring any other disease to their children or even could make them sterile and may cause death. These common believes among them was the major impediment regarding polio drops intake (Khan & Qazi, 2013). Situation is not similar in present study as majority of our study respondents have knowledge about polio, vaccinating their children, ensure cooperation with polio workers and know that this is a treatable disease.
When we discuss perceptions regarding polio, myths about vaccination can only be eliminated by creating awareness among people. The role of health care specialists can play a vital role. The need of hour is to ensure parents that it would be helpful in safety of their children’s health, because safety of their children is of prime importance for parents. So, health experts should ensure positive impact of vaccination for their children. Furthermore, negative perceptions can be made positive only when it (vaccine) is proved more advantageous than risks to health (Song, 2014). Many factors influence the perception of people regarding passive immunization or vaccinations. These factors include: Socio-economic status, controversies about vaccination among people, unawareness and parental attitude. The only way to combat all factors that influence the use of vaccine is to provide awareness among parents and educating them about positive use of vaccine. Apart from several controversies, many religious controversies were found arising as in Nigeria and India in 2003 and 2006 respectively. These controversies affected campaigns of vaccination. Religious leaders can play a role to overcome religious controversies about immunization (Lorenz & Khalid, 2012). Our study unveils that our respondent’s perception about perception of this disease is different from previous studies. Results of present study represent that 89percent of our sample perceived that polio vaccination is good for our children. Very few cases were of the view that it will affect the fertility level. Lack of immunization will be a major reason for higher degree of risk or polio interaction and 48percent of our respondents said that contact with infected person may increase the chances of getting infected.
Perception or misconception in case of present study results never matches with previous studies. As stated by Abid et al., (2010) that the major impeding factor in eliminating poliomyelitis is the delusion spread among people. The myths about intake of vaccination get more rigorous when based upon religious belief or antagonist to the norms of society. Several religious extremists or other organizations might play central role in the dissemination of misconception of immunization which ultimately lessens the number of recipients (Karamat, 2012; Khan & Qazi, 2013). Amongst other indicators of culture, beliefs of people are strongly structured by religion. Thus, religion plays integral role which can be used for creating awareness among people regarding health. This can be proved by a research conducted in India, which stated that increase in intake of vaccine was seen when they involve religious leaders in it. It resulted in a positive output which can be identified by decrease in number of those who were refusals of taking vaccine. Within 2 years the number of people who were opponents of taking passive immunization dropped through vaccine from 5% to 0%. Similar outcomes were noticed in Pakistan by involvement of religious leaders (Obregon et al., 2009).
Another indicator that relates to high risk of polio is education of mothers. All misconceptions resulted in changing attitude of people towards vaccination. The attitude of a mother is needed to be addressed here because of their concern regarding their children’s health. Research studies showed that their belief about misconceptions was all the same whether they were educated or not. But education plays a vital role; educated mothers were found having more awareness about health, health care centers and other facilities. Above all, they need to build a trust level among parents regarding facilities provided by health care services (Streatfield et al., 1990).
Conclusion
Findings of our study are not similar to the results of previous studies conducting in tribal or remote areas of Pakistan. More than 90% parents know what polio is, 55% mentioned TV as information source, 81% of the view that polio is a health concern, and 93% argued that virus causes permanent disability among children In Pakistan, an inclusive approach is needed to end poliomyelitis as whole (Bhutta, 2014). Polio and its eradication should not be the sole target but health of mother and child should be the goal to have positive outcomes to eliminate all means of infectious diseases such as polio. Thus, it should be included in strategies adopted to improve mother-child health (Habib et al., 2016). Present study found that situation regarding, awareness, perception and practices to overcome polio from Pakistan is much better than tribal or remote areas of Pakistan. People are well aware of disease, its spreading patterns, how we control it, how we cooperate with polio teams to eradicate this.
References
- Abid, N., Islam, O. U., Bosan, A., Iqbal, T., Darwish, A., and Bile, K. M. (2010). Pakistan's fight against poliomyelitis: Introducing innovative strategies to address challenges and attain the goal of eradication. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 16, S5-14.
- Ali, A., Ali, L., Shah, M., Khan, N., Shafee, M., Jan, & S. K. (2018). Polio vaccination; an analysis of cultural and traditional barriers. Professional Med J ;25(1):67-72. DOI:10.29309/TPMJ/18.4158
- Baloch, S. M. (Jun-02-2020). Pakistan polio fears as Covid-19 causes millions of children to miss vaccinations. access date: 13-06-2020
- Basharat R. (April-19, 2020). 40 million children miss polio vaccinations due to COVID-19. Access date: 13-06-2020
- Bhutta, Z. A. (2014). Infectious disease: Polio eradication hinges on child health in Pakistan. Nature, 511(7509), 285-287.
- End Polio, (2019). Eradication Polio in Pakistan. access date: 10-06-2020
- Habib, M. A., et al., (2016). Knowledge and perceptions of polio and polio immunization in polio high-risk areas of Pakistan. Journal of Public Health Policy. DOI: 10.1057/s41271-016-0056-6
- Janjua, H. (May-08, 2020). Pakistan's fight against COVID-19 threatens polio, measles vaccine programs. Access date: 13-06-2020
- Karamat, K. A. (2012). Prevalence and control of polio myelitis in Pakistan. Planning Commission of Pakistan. Available at , accessed on 10 September 2016.
- Khan, M. U., Ahmad, A., Aqeel, T., Salman, S., Ibrahim, Q., Idrees, J., & Khan, M. U. (2015). Knowledge, attitudes and perceptions towards polio immunization among residents of two highly affected regions of Pakistan. BMC Public Health; 15(1):1-9.
- Khan, T., & Qazi, J. (2013). Hurdles to the global antipolio campaign in Pakistan: an outline of the current status and future prospects to achieve a polio free world. Journal of epidemiology and community health.; 67(8):696-702.
- Lorenz, C., & Khalid, M. (2012). Influencing factors on vaccination uptake in Pakistan. Journal of Pakistam Medical Association. 62(1):59-61.
- McCombes, C. (2019). Descriptive research. Access date: 13-06-2020
- Mukhtar, I. (May-18, 2020). In Pakistan, missed immunisations drive new disease fears. Access date: 13-06-2020
- Obregón, R., Chitnis, K., Morry, C., Feek, W., Bates, J., Galway, M., & Ogden E. (2009). Achieving polio eradication: a review of health communication evidence and lessons learned in India and Pakistan. Bulletin of the World Health Organization; 87(8): 624-630.
- Polio Eradication. Surveillance 2017. (Accessed 21.02.2017).
- Roberton, T., et al., (May-12-2020). Early estimates of the indirect effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and child mortality in low-income and middle-income countries: a modelling study. Lancet Global Health 2020; (published online May 12.) doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30229-1
- Sanjari, M., Bahramnezhad, F., Fomani, F. K., Shoghi, M., & Cheraghi, M. A. (2014). Ethical challenges of researchers in qualitative studies: the necessity to develop a specific guideline. Journal of medical ethics and history of medicine :7.14
- Song, G. (2014). Understanding public perceptions of benefits and risks of childhood vaccinations in the United States. Risk Analysis, 34(3):541-555.
- Streatfield, P. K., et al., (1990). Maternal Education and Child Immunization. Demography;27(3):447-55. DOI: 10.2307/2061378
Cite this article
-
APA : Chaudhry, A. G., Ahmed, A., & Hayat, U. (2020). Polio Endemic: Perceptions and Practices from Sohan Village, Islamabad. Global Political Review, V(I), 62-71. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpr.2020(V-I).08
-
CHICAGO : Chaudhry, Abid Ghafoor, Aftab Ahmed, and Umer Hayat. 2020. "Polio Endemic: Perceptions and Practices from Sohan Village, Islamabad." Global Political Review, V (I): 62-71 doi: 10.31703/gpr.2020(V-I).08
-
HARVARD : CHAUDHRY, A. G., AHMED, A. & HAYAT, U. 2020. Polio Endemic: Perceptions and Practices from Sohan Village, Islamabad. Global Political Review, V, 62-71.
-
MHRA : Chaudhry, Abid Ghafoor, Aftab Ahmed, and Umer Hayat. 2020. "Polio Endemic: Perceptions and Practices from Sohan Village, Islamabad." Global Political Review, V: 62-71
-
MLA : Chaudhry, Abid Ghafoor, Aftab Ahmed, and Umer Hayat. "Polio Endemic: Perceptions and Practices from Sohan Village, Islamabad." Global Political Review, V.I (2020): 62-71 Print.
-
OXFORD : Chaudhry, Abid Ghafoor, Ahmed, Aftab, and Hayat, Umer (2020), "Polio Endemic: Perceptions and Practices from Sohan Village, Islamabad", Global Political Review, V (I), 62-71
-
TURABIAN : Chaudhry, Abid Ghafoor, Aftab Ahmed, and Umer Hayat. "Polio Endemic: Perceptions and Practices from Sohan Village, Islamabad." Global Political Review V, no. I (2020): 62-71. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpr.2020(V-I).08