Abstrict
Social media has got a major share in our personal as well as professional communication because of its easy accessibility and highly interactive nature. Facebook and Twitter can be used as important tool to mobilize groups to take some action (Shirky, 2008, p. 184). It has been observed that political leaders in Pakistan use social media to connect with the audience, but no research has been conducted in this regard so far. Therefore, the main objective of this study is to find which platform does the political actors of Pakistan prefer to disseminate information and in which medium they believe more. Furthermore, this study also looks into the popularity graph of the politicians, whether the use of social media has increased their popularity or not. To fulfil the objectives of the study, the survey was conducted among the members of national and provincial assemblies (2013-2018). With the help of findings, it was concluded that the majority of the politicians in Pakistan prefer Facebook over Twitter when they want to share any information, which is unlike the scenario around the globe.
Keywords
Politicians, Facebook, Twitter, Pakistan, Strategic Communication
Introduction
Facebook and Twitter are becoming an important part of our lives; it has started influencing the way we talk to each other, the way we socialize and even the way we utilize our time. Social media has got a major share in our personal as well as professional communication because of its easy accessibility and highly interactive nature. Facebook and Twitter can be used as important tool to mobilize groups to take some action (Shirky, 2008, p. 184). It is quite impossible to challenge the importance of social media; in fact, its fast growth is challenging the norms and values of traditional media by putting a question mark on the way it is used to spread any message and to begin any debate on any important political and social issues (Yang, Chen, Maity, & Ferrara, 2016). The social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook have created innovative styles to influence, connect, and engage other citizens (Grant, Moon, & Busby, 2010).
Furthermore, Stieglitz and Dang-Xuan (2012) reported that Facebook and Twitter possess the ability to influence any political discussion and participation in a positive manner. The political actors are making full use of social media as an emerging tool to enhance communication and exchange of viewpoint with the public. The most important factor and advantage here is that the information flows directly from politicians’ mind to the target audience through Facebook and Twitter. The various researches have revealed that the politicians trust the effectiveness of social media, and their basic goal is to reach out to a maximum number audience in less time. Mengü, Güçdemir, Ertürk, and Canan (2015) also stated social media is favorable for the politicians because of its easy accessibility and steadfast usage.
The use of Twitter by US President Donald Trump during his election campaign and even after acquiring the office has shown that Twitter was the most preferred social media platform of US president. He followed the footsteps of Barack Obama and put a lot of effort into connecting to people through Twitter which clearly paid him off. He had a huge following, and his tweets do have an impact on the audience and sometimes motivates them in the desired direction.
There is no doubt that content produced on micro-blogging service like Twitter can positively influence political participation; that is why Twitter considered being the perfect platform for self-promotion. It also gives an opportunity to the political actors to inform the target audience regarding their political and personal activities without any delay. Politicians can motivate people to take action in the way they want. Most of the scholars believe that Twitter enjoys the privilege of being the most trustworthy platform as far as communication for political gains is concerned. It is believed that Twitter is the medium having distinctive qualities that, unlike all other social media platforms, allow the consumers and brands to let loose, manage relationships, and enhance engagement. But Twitter is different from Facebook because it is bold and asymmetric. All other conventional social platforms are more confined to the people whom we already know, and information and updates are less visible.
As in the last few years, many politicians are utilizing Twitter to achieve political objectives, so with its recent popularity, the relationship of Twitter with politics has been the subject of various research studies (Aharony 2012). The information flows directly from the mouth of the politicians to the voters’ Facebook and Twitter pages.
Twitter has different capabilities; unlike other social media platforms, it allows us to build relationships and optimize engagement. In the last few years, many politicians incorporated Twitter into their campaigns. Because of the increased popularity of Twitter, the impact of Tweets of politicians on the audience has been a subject of numerous researches. The literature review shows that the politicians in the world prefer Twitter to disseminate information, but the preference of Pakistani politicians is still unknown. The use of the internet, knowledge about politics and participation are very much interlinked. This trend is playing a key role in elections, especially in developing countries like Pakistan, India, and Bangladesh. (McAllister, 2015). It has been observed that political leaders in Pakistan use Twitter to connect with the audience, but no research has been conducted in this regard so far. Therefore, the main objective of this study is to find which platform do the political actors of Pakistan prefer to disseminate information and in which medium they believe more. Furthermore, this research also investigates that do political actors think that usage of social media has increased the popularity of the political actors. The research questions for this study are as follows:
RQ 1. Which social media platform is being preferred by the politicians of Pakistan to connect with their audience?
R.Q.2. Which social media platform is considered more credible and authentic to get information from the politicians of Pakistan?
R.Q.3. Do the politicians believe that usage of social media has increased their popularity among the audience?
Political Communication and Social Media
Social media has introduced a few alterations and shifts in political communication. These outlets are now
valued resources being utilized by political leaders to enhance their presence. Social media is developed as an indispensable way to communicate and has generated up to date tools of political mobilization, motivating “social media users” to involve in political events, including developing links with their respective political parties and following the status updates.
Stieglitz, Brockman and Dang-Xuan (2012), in reference to the political sector, stated social media could infuse participation and democracy among the citizens. The politicians and political parties require a constant presence on the social media networks to elevate the image and nourish two-way, real communication with the potential voters and supporters. As social media energizes both two and one-way communication, it provides a chance to develop a dialogue among the greater audience; social media is most suitable to cultivate relationships. As it makes it convenient to respond and sometimes even conclude the discussion. Thus, politicians should use it strategically; if they want to take the maximum benefit of social media, they should use it strategically.
Strategic Communication through Social Media
Chadwick, Galley, Karlsen, & Enjolras (2016) were of the view that the thoughtful engagement of communication by a body to meet its aim is known as strategic communication. The politicians should include themselves in two-way communication because using Facebook and Twitter for only one-way information distribution is of no benefit. This channel is not only important for the purpose of strategy to build and maintain their relationship with the target group but also to grow their own connection with the audience directly themselves. Politicians find social media as a more direct and easier channel of communication and interaction with their audience as it evades the severely intervened checks that the traditional media offers (Hallahan, Holtzhausen, Sriramesh, Ver?i?, & Van Ruler 2007); furthermore, it also helps politicians to “attract the audience’s notice” (Graham, Jackson & Broersma 2016), making it a huge prospective for strategic communication. The power of social media through which political parties can communicate, interact, mobilize, raise funds and change perspective according to their agenda are some of the very important benefits strategically for their politics (Johnson, 2011).
Undoubtedly, the role of social media in politics is very important, especially for strategic communication and political campaigns, as it can offer as a channel to convey policy preferences, opinions, agendas and perspectives of politician actors/parties to their target audience (Nulty, Theocharis, Parnet, & Benoit, Popa, 2016).
Using Political rhetoric through social media in order to persuade their audience the way they want is one of the strategies used by political actors (Jalilifar & Alavi, 2012, p. 44), Twitter and, in certain cases, Facebook also is considered prime tools of social media for self-promotion and giving political actors the option to communication big number of people about their political campaigns almost directly, hence making them a part of political public relations (Aharony, 2012). Political parties and politicians are using social media significantly to approach their political units and voters. Almost all units of government, including Ministers, Opposition Leaders and other political actors, are communicating directly to their audience in an accurate manner through Social Networking Sites (SNS), especially Twitter and Facebook.
It has been studied in the case of Pakistan, the politicians and political actors are utilizing SNS to gain some strategic objects to grow the relationship between their parties and their target public. However, not much research has been done on the aim and efficacy of their strategic communication. Some of the purposes of using social media by the Political actors and public are to communicate, build a relationship, boost digital engagement through likes and shares, which eventually adds to their presence in the audience.
For the last many years, social media has been utilized for political communication strategically. The political participation of the audience is continuously enhancing through SNS. Today, the politicians are operating their own official Facebook pages and enjoying direct interaction with their public. The politicians post about their activities and receive instant reaction/response from their constituents. In this modern age, social media is one of the most popular forms of digital media. People spend their time on Facebook, Twitter and Linked In, etc., to stay in contact with others, no matter where they are sitting. These are the platforms considered more accessible for sharing the happenings, viewpoint, attitudes, reactions and also, these are the innovative forums for heated discussions and new debates. About more than 2.19 billion people are members of Facebook, whereas around 336 million people have Twitter accounts around the globe (Steiglitz, Brockmann, & Xuan, 2012).
Chun, Shulman, Sandoval, & Hovy (2010) asserted that the political leaders and officials use Twitter to influence the audience and have more impact than the press conferences and press releases which are now considered as the traditional forms of information dissemination. Politicians use social media platforms to convey messages to the larger audience (Chun & Warner 2010; Chun et al. 2010) Shogan (2010) reinforced that SNS have the capacity to modify and alter the communication strategies. It is very much obvious that in a short period, the politicians in contemporary democratic states all over the globe are using Facebook and Twitter to reach the target public (Gulati & Williams, 2010).
Methodology
To answer the research questions, the survey was conducted among the politicians of Pakistan. The study focuses on members of National and Provincial Assemblies during 2013-2018. One of the major limitations of this study was to access the politicians; many of them were reluctant and not ready to respond to the questionnaire. That is why the respondents who were willing to participate in the survey were included; thus, the sample was drawn while using the purposive and convenience sampling technique. The list of the members of the National and Provincial assemblies was taken from the assembly offices, the members were the contact, but all of them were not willing to be a part of the study. Therefore, in total, 247 political actors from the provinces and Capital city responded to the questionnaire, 40 from National Assembly, 110 from Punjab, 38 from Sindh, 36 from Baluchistan, and 23 from KPK. The questionnaires which were designed for the study were then to the contact persons who were deputed in Lahore, Quetta, Peshawar, Karachi and Islamabad. It was kept in mind while deputing the focal persons that they should have access to the assemblies, and they were known to the politicians. The questionnaire was intentionally kept simple and brief with more close-ended questions.
Findings and Interpretation
Where Political Actors Share Information First
Social media is now known as an influential platform to distribute information, and to fulfil this purpose, Facebook and Twitter are taken as the most popular platforms.
The political actors of Pakistan are also known to social media and use it to disseminate information among their public; it was imperative to know which platform they think is more
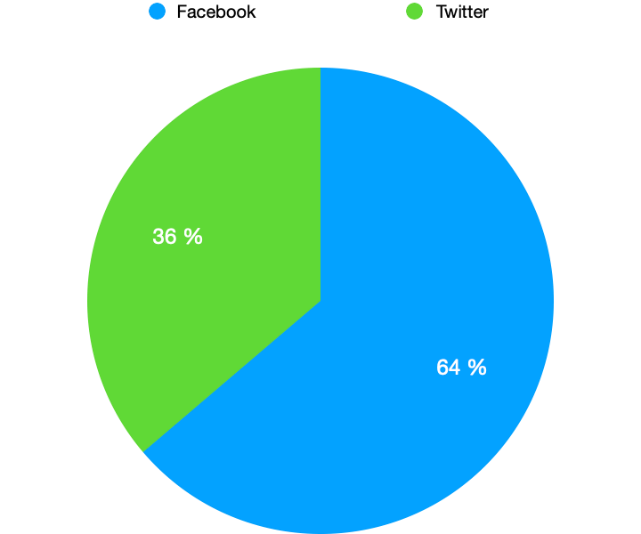
Figure
1: Where Political Actors Share Information First
appropriate for strategic communication with the public and which platform they prefer to share their information to point out the preferred medium for sharing of their personal and political information, the question about their priority was asked. Figure 1 shows that according to 64% of respondents, Facebook is the place where they share their information first, which is way higher than Twitter, i.e. 36%. This shows the preferences of the politicians of Pakistan very clearly.
Is Social Media a Better Way to Communicate
It has been revealed in many studies that social media provides an opportunity for politicians to interact with their audience directly without any bridge or middleman (Kushin, &Yamamoto, 2015). Hence, to analyze the behavior of Pakistan’s politicians, it was important to know whether they think that social media is a better way to communicate with the audience. The findings in Figure 2 shows the reaction of the politicians on the question regarding the information received from social media, 12 % of respondents strongly agreed, 44 % showed agreement that social media is a much better way to communicate, only 13% disagreed and 28% neither agreed nor disagreed.
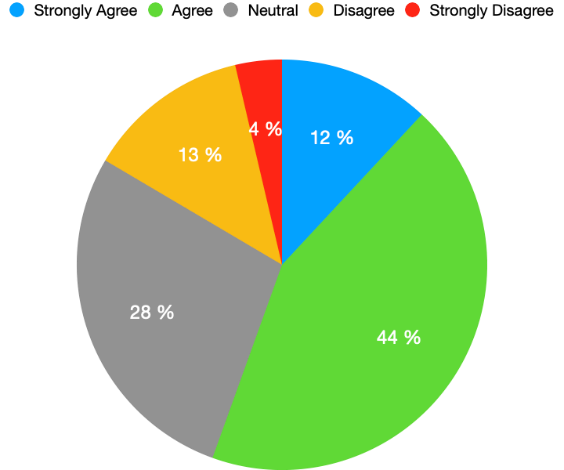
Figure 2: Social Media is a Better Way to Communicate
Believe in news/information through Facebook
To know the behavior of Pakistan’s political actors, it was important to know whether they believe in any information they get from Facebook. The findings in Figure 3 shows the opinion of the political actors regarding the information received from Facebook, 8 % of respondents strongly agreed and 45 % agreed that they believe in information they get from Facebook, only 8% disagreed, and 36% remained neutral on this.
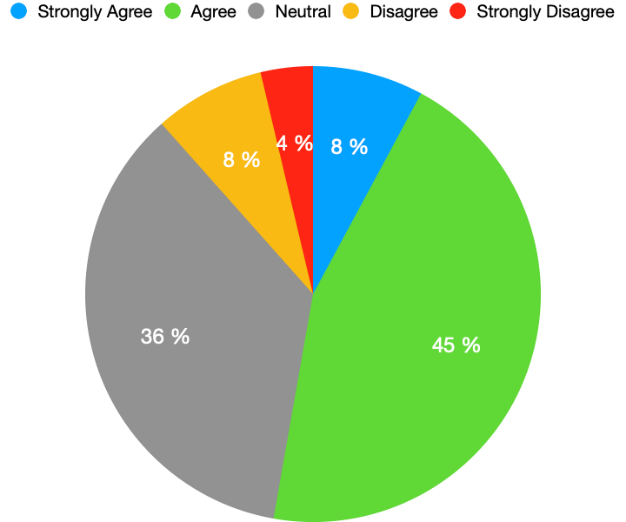
Figure 3: Belief in news/information through Facebook
Believe in News/Information through Twitter
When the same question was asked from the politicians about Twitter, according to the results in Figure 4, 17% agreed that they believe in information they get through Twitter, whereas 10% strongly agreed, 17% disagreed, 3 % strongly disagreed, and 52 % neither agreed nor disagreed. These results clearly show that the politicians of Pakistan considered Facebook more reliable as compared to Twitter which is a slightly different phenomenon is seen in the light of the literature review.
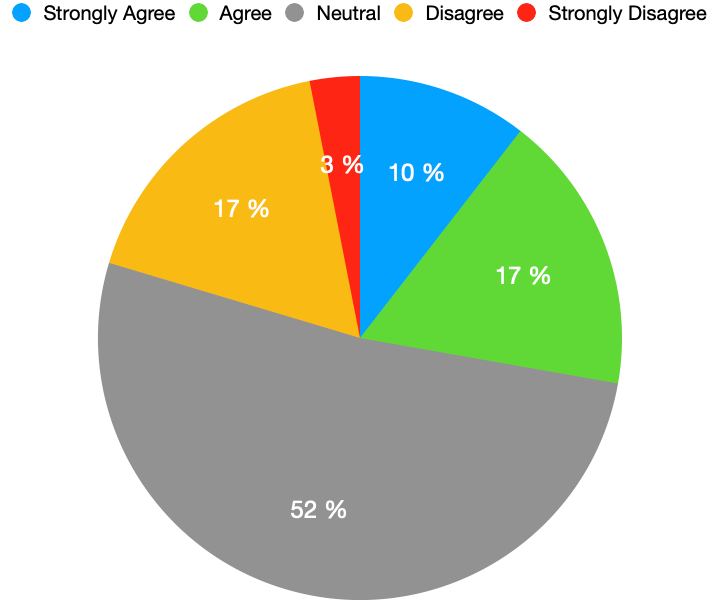
Figure 4: Belief in news/Information through
Twitter
Twitter is a more authentic and Credible mean of communication
Likewise, the political actors were asked do they consider Twitter a more authentic and credible mean of communication; 36% agreed, 12 % strongly agreed, 18% disagreed, only 1% strongly disagreed, and 34 % remained neutral (Figure 6).
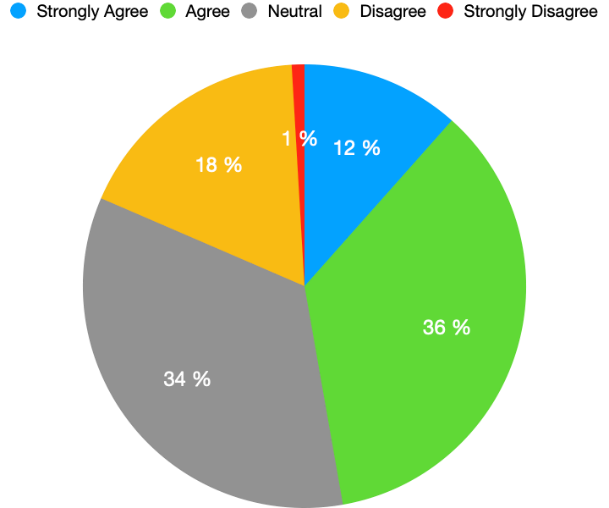
Figure 6: Twitter is a more authentic and Credible mean of communication
Facebook and Twitter have Increased popularity
It was interesting to find out that whether the politicians think that social media has any impact on their popularity or not because they are directly connected with the audience, the result (Figure 7) shows that 36% of political actors agreed that social media increased their popularity whereas 12% strongly agreed, 18% disagreed and 1% strongly disagreed with the notion that Twitter and Facebook increased their popularity.
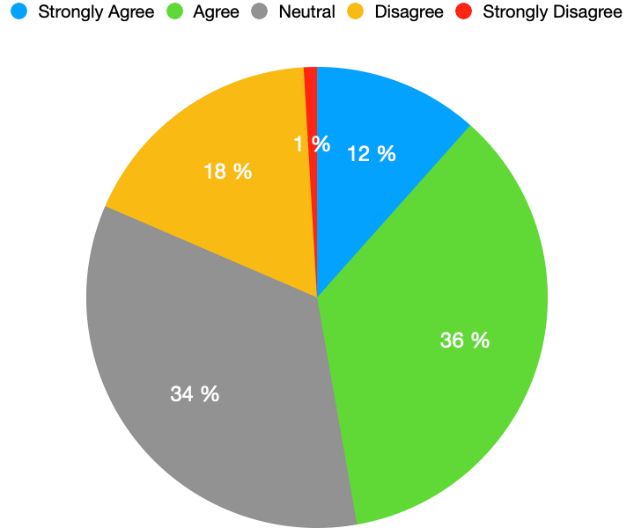
Figure 7: Facebook and Twitter have increased the popularity
Discussion and Conclusion
All over the world, the use of the internet is now necessary to keep political discussions alive and enhance political participation. A few years ago, the political parties and the politicians were using websites to inform their public, which is a one-way communication tool. It was used only for information spread; there was no provision for discussion, feedback and direct communication. However, new media and technology have changed communication patterns in two-way communication (Emruli & Ba?a, 2011). This study was an exploratory study intended to find about the usage and preferences of the politicians of Pakistan when it comes to social media. The basic objective behind this is to explore which social media platform is more preferable for the politicians of Pakistan and where they want to share the information first.
The findings of this study show that the politicians were investing more time on Facebook than Twitter; however, the situation is other parts of the world is quite contrary. Politicians around the globe rely more on Twitter than Facebook; the reason behind this can be the “asymmetric” nature of Twitter which makes it potentially more conducive for political interaction (Porter, 2009). Besides all this discussion, the noteworthy point is that Pakistani politicians have at least accepted the importance of social media and technology and have inculcated it in their communication with their target audience. Figure 1 shows that the majority of the political actors, i.e. 64 % preferred to share information on Facebook, whereas only 36 % wanted to share information on Twitter first. Likewise, 45 % agreed that they believe in information they get through Facebook, whereas only 17 % of responses agreed that they believe in information they get through Twitter. This is a very interesting phenomenon because Twitter has been considered an official platform for many political parties and organizations, whereas Facebook is considered a more personal socializing platform, but the politicians here in Pakistan rely more on Facebook to get information. We can also infer from this that the politicians in Pakistan are still exploring social media and experimenting.
It has been discussed in many researches that social media has challenged the way traditional media has been used to disseminate information and to discuss social and political issues (Yang, Chen, Maity, & Ferrara, 2016). To reveal the real situation in Pakistan, it was asked form the politicians whether they think that social media is a better way of communication or not, 44 % of respondents were in favour that social media is a better way to communicate, 12 % strongly agreed whereas only 13 % considered traditional media a better way of communication as compared to social media. As the percentage of respondents against the use of social media is not much higher, it can be stated that politicians are embracing social media as an alternate and more direct way of communication. Meanwhile, the majority of the respondents agreed that social media had increased their popularity among the audience. There can be many reasons behind this notion, maybe because social media provides the opportunity to interact with the people and share personal as well as political information with them so there is more sense of closeness and as they can get the feedback immediately from the audience so the politicians can also keep track of their popularity graph.
With the help of findings, it can be safely concluded that in Pakistan, politicians are taking advantage of social media; they are interacting with people through Facebook and Twitter, they are using it for their political communication. But if we compare the trend of preferences and usage in Pakistan with the trends going on in the world, it can be suggested that the politicians here need to pay attention to Twitter more if they want to communicate strategically with the audience, cultivate a long-lasting relationship with them and manage their reputation.
References
- Aharony, N. (2012). Twitter use by three political leaders: an exploratory analysis. Online Information Review, 36(4), 587-603. doi: 10.1108/14684521211254086.
- Bertot, J. C., Jaeger, P. T., Munson, S., & Glaisyer, T. (2010). Social media technology and government transparency. Computer, 43(11), 53-59. doi: 10.1109/MC.2010.325
- Chadwick, A., Stromer-Galley, J., Karlsen, R., & Enjolras, B. (2016). Styles of social media campaigning and influence in a hybrid Broersma political communication system. The International Journal of Press/Politics, 21(3), 338-357. doi:10.1177/194016121664 5335
- Chun, S., Shulman, S., Sandoval, R., & Hovy, E. (2010). Government 2.0: Making connections between citizens, data and government. Information Polity, 15(1, 2), 1-9.
- Chun, S., & Warner, J. (2010). Finding information in an era of abundance: Towards a collaborative tagging environment in government. Information Polity, 15(1, 2), 89-103. doi:10.3233/IP-2010-0201
- Emruli, S., BaÄÂa, M. (2011). Internet and political communication-Macedonian case International Journal of Computer Science, 8, 154-163.
- Graham, T., Jackson, D., & Broersma, M. (2016). New platform, old habits? Candidates' use of Twitter during the 2010 British and Dutch general election campaigns. New media & society, 18(5), 765- 783. doi: 10.1177/1461444814546728
- Grant, W. J., Moon, B., & Busby G., J. (2010). Digital dialogue? Australian politicians' use of the social network tool Twitter. Australia
- Gulati, J., & Williams, C. B. (2010). Communicating with constituents in 140 characters or less: Twitter and the diffusion of technology innovation in the United States Congress.
- Hallahan, K., Holtzhausen, D., Van Ruler, B., VerÄÂiÄÂ, D., & Sriramesh, K. (2007). Defining strategic communication. International journal of strategic communication, 1(1), 3-35. doi: 10.1080/15531180701285244
- Jaeger, P. T., & Bertot, J. C. (2010). Transparency and technological change: Ensuring equal and sustained public access to government information. Government Information Quarterly, 27(4), 371-376. doi:10.1016/j.giq.2010.05.003
- Jalilifar, A. R., & Alavi, M. (2012). Power and politics of language use: A survey of hedging devices in political interviews. Journal of Teaching Language Skills, 30(3), 43-66. doi: 10.22099/JTLS.2012.377.
- Johnson, D. W. (2011). Campaigning in the twenty-first century: A whole new ballgame? New York, NY: Routledge.
- Kushin, M. J., & Yamamoto, M. (2010). Did social media really matter? College students' use of online media and political decision making in the 2008 election. Mass Communication and Society, 13(5), 608-630. doi: 0.1080/15205436.2010.516863
- McAllister, I. (2015). Internet use, political knowledge and political participation among young voters in Australia. The Conference Democracy: A Citizen Perspective. Finland: Åbo Akademi University
- Mengü, S. Ç., Güçdemir, Y., Ertürk, D., & Canan, S. (2015). Political preferences of generation Y university student with regards to governance and social media: A study on March 2014 local elections. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 791-797. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.616
- Nulty, P., Theocharis, Y., Popa, S. A., Parnet, O., & Benoit, K. (2016). Social media and political communication in the 2014 elections to the European Parliament. Electoral Studies, 44, 429-444.
- Petrova, M., Ananya, S. & Yildirim, Pinar (2020, May 14)) Social Media and Political Contributions: The Impact of New Technology on Political Competition. Management Science
- Porter, J. (2009). Relationship Symmetry in Social Networks: Why Facebook will go Fully Asymmetric.
- Shirky, C. (2011). The political power of social media: Technology, the public sphere, and political change. Foreign affairs, 28-41.
- Shogan, C. J. (2010). Blackberries, tweets, and YouTube: Technology and the future of communicating with Congress. PS: Political Science & Politics, 43(2), 231-233. doi:10.1177/0893318905282208
- Stieglitz, S., Brockmann, T., & Dang-Xuan, L. (2012,). Usage of Social Media for Political Communication. PACIS.
- Stieglitz, S., & Dang-Xuan, L. (2012). Political communication and influence through microblogging--An empirical analysis of sentiment in Twitter messages and retweet behavior. In System Science: 45th Hawaii International Conference on (pp. 3500-3509). doi: 10.1109/HICSS.2012.476
- Yang, X., Chen, B. C., Maity, M., & Ferrara, E. (2016). Social politics: Agenda setting and political communication on social media. International Conference on Social Informatics, 10046, 330-344. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47880-7_20
Cite this article
-
APA : Shami, S., Toor, S. I., & Ashfaq, A. (2020). Social Media and Strategic Communication: Uses and Preferences of the Politicians of Pakistan. Global Political Review, V(III), 80-89. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpr.2020(V-III).08
-
CHICAGO : Shami, Savera, Shazia Ismail Toor, and Ayesha Ashfaq. 2020. "Social Media and Strategic Communication: Uses and Preferences of the Politicians of Pakistan." Global Political Review, V (III): 80-89 doi: 10.31703/gpr.2020(V-III).08
-
HARVARD : SHAMI, S., TOOR, S. I. & ASHFAQ, A. 2020. Social Media and Strategic Communication: Uses and Preferences of the Politicians of Pakistan. Global Political Review, V, 80-89.
-
MHRA : Shami, Savera, Shazia Ismail Toor, and Ayesha Ashfaq. 2020. "Social Media and Strategic Communication: Uses and Preferences of the Politicians of Pakistan." Global Political Review, V: 80-89
-
MLA : Shami, Savera, Shazia Ismail Toor, and Ayesha Ashfaq. "Social Media and Strategic Communication: Uses and Preferences of the Politicians of Pakistan." Global Political Review, V.III (2020): 80-89 Print.
-
OXFORD : Shami, Savera, Toor, Shazia Ismail, and Ashfaq, Ayesha (2020), "Social Media and Strategic Communication: Uses and Preferences of the Politicians of Pakistan", Global Political Review, V (III), 80-89
-
TURABIAN : Shami, Savera, Shazia Ismail Toor, and Ayesha Ashfaq. "Social Media and Strategic Communication: Uses and Preferences of the Politicians of Pakistan." Global Political Review V, no. III (2020): 80-89. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpr.2020(V-III).08
